Loopr Docs
By GekocaretakerLoopr is a program that allows you to write hundreds of lines of similar-looking code very quicky.
The Basics
Loopr currently has two different modes, Loop Through a List and Loop Total Times. Each one has a different data input, which will be talked about in Loop Through a List and Loop Total Times Both have a template field (See Output Template) and a finished loop field. There are 5 additional buttons:- Generate: Used to generate your loop using the template and data.
- Copy Output: This allows you to easily get the output of your loop without needing to highlight it all.
-
Save: Export your loop to work with later. Saves as a
.lprfile - Load: Load your loop from a saved
.lprfile. - Share: Send your loop to someone else as a url.
Loop Through a List
Use a list of values to get a different output loop. Each value needs to be separated with a newline character (Enter Key). The list of values will go into the list field. The data input of this is<<value>>
Loop Total Times
Use a number to loop. The data input of this is<<length>> and <<line>>
Output Template
The template is what the data will be added to, so it can make variations of the template in the output. The template has a special scripting system using<< >>. Here is valid scripts:
- value [String]: The current value from the list. Only usable in Loop Through a List.
- line [Number]: The current position of the loop. Usable in all loopr modes.
- length [Number]: The amount of items in a list in Loop Through a List or is the total amount of loops in Loop Total Times
- parseFloat(value) [Number]: Used to convert the current value into a float to work with math. Can throw an error if the value can't be converted.
-
Operations of Mathematics: You can use
+,-,*,/, and% - Math: The Math class can be used for complicated mathematics.
- Infinity: This only writes the word Infinity.
- Date: The Date class can be used to work with date and time.
- RegExp: The RegExp class can be used to modify strings using either literal notation or the class itself.
-
Conditionals and Loops: You can use
if,else,switch,case,for, andwhile
Examples:
Minecraft Bedrock JSON: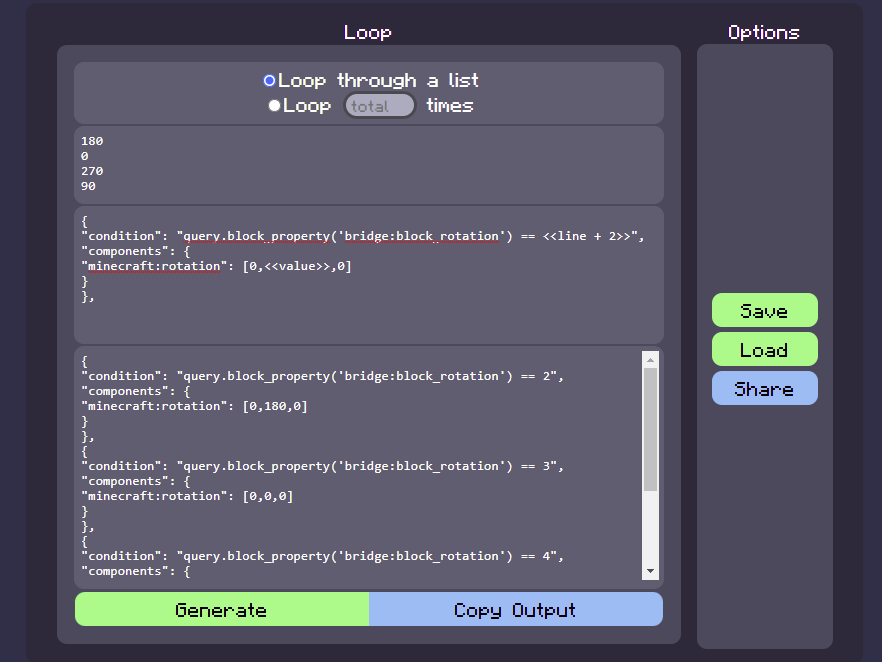
Using the
% operator to determine if a number is even and also displaying the progress of the loop: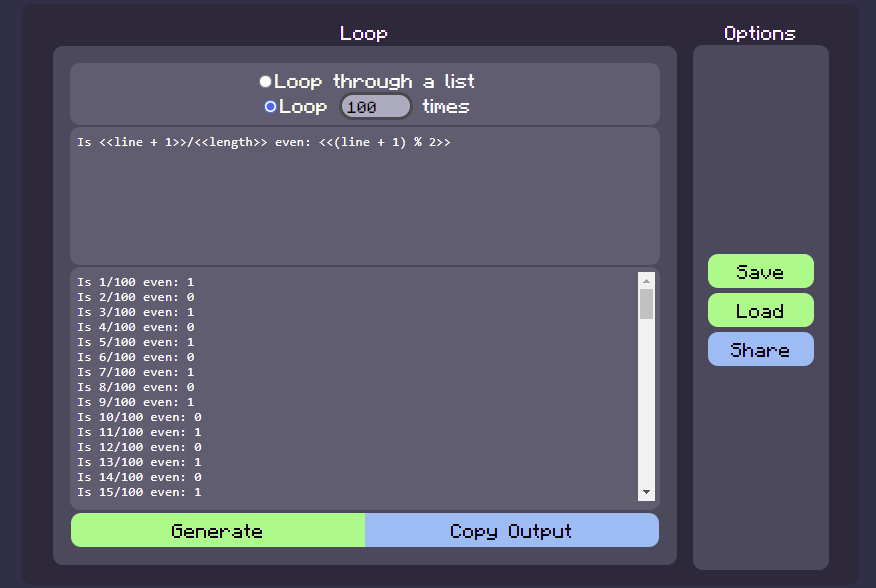
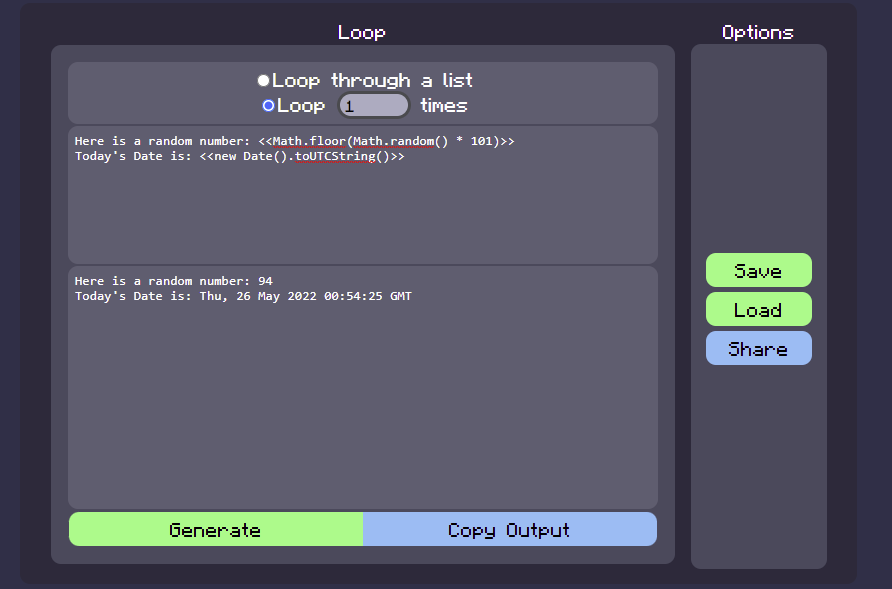
Example using Math and Date: